A Beginner’s Guide to Google Search Console

If you run a website, you’ve probably heard of Google Search Console (GSC) before. For many website owners, GSC’s insights are treated as gospel for website maintenance and performance.Like Google Analytics, it’s a completely free tool that can significantly improve your site’s performance when used correctly.
In this article, we’ll explain what Google Search Console is, how to use it for SEO, and why it’s important for anyone managing a website.
What is Google Search Console and why should you use it?
Google Search Console is a completely free service from Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your website’s presence in Google search engine results (SERPs).
While you don’t necessarily need a GSC account to rank in Google SERPs, having one can provide valuable insights into how Google views your site, helping you improve your ranking.
If you haven’t guessed already, Google Search Console is essential if you want to rank higher on search engine results. Anyone who runs a website can benefit from GSC, including:
- Business owners
Whether you manage your website yourself or have employees handling it, it’s important to understand how Google Search Console can help. Familiarizing yourself with its features can optimize your site for better SERP rankings. - Search engine optimizers or marketers
Unsurprisingly, if you work in marketing, GSC is an invaluable tool. It helps monitor website traffic and improve rankings. It also provides insights that allow you to make informed decisions on technical website performance, and it pairs well with other Google tools like Analytics, Google Trends, and Google Ads. - Site administrators
Site administrators rely on GSC to keep their sites running smoothly. It alerts you to server errors, site load issues, and security problems like hacking or malware. You can also use GSC to ensure stable performance during routine site maintenance. - Web developers
If you’re building a site with markup and/or code, GSC provides insights to help monitor and fix common markup issues, such as errors in structured data.
What are the main features of Google Search Console?
Google Search Console can do a lot, but you might wonder what features help you improve your SERP rankings, and technical performance, or conduct deeper marketing analysis. Let’s find out!
Here is a quick overview of its main features as of January 2026:
- Performance report: Tracks search queries, clicks, impressions, and average position.
- URL inspection tool: Checks indexing status and identifies crawl errors.
- Coverage report: Shows which pages are indexed and helps troubleshoot indexing issues.
- Sitemaps: allows submission and management of XML sitemaps.
- Mobile usability report: Identifies mobile-friendly issues and provides optimization recommendations.
- Core web vitals report: Measures key user experience metrics like LCP(Largest Contentful Paint), FID(First Input Delay), and CLS(Cumulative Layout Shift).
- Security issues: Alerts for potential security problems like hacking or malware.
- Links report: Shows internal and external links to your website.
- Manual actions: Notifies about manual penalties from Google.
- Removals: Allows temporary removal of URLs from search results.
- Data highlighter: Helps mark up structured data on your site.
- Search analytics: Provides detailed insights into search performance and user behavior.
How to connect Google Search Console

If you already have a Google account, you can set up a Google Search Console account very quickly. Here’s how you can get started in 5 steps:
1. Go to Google Search Console and click “Start now.”
2. Log in with your Google account.
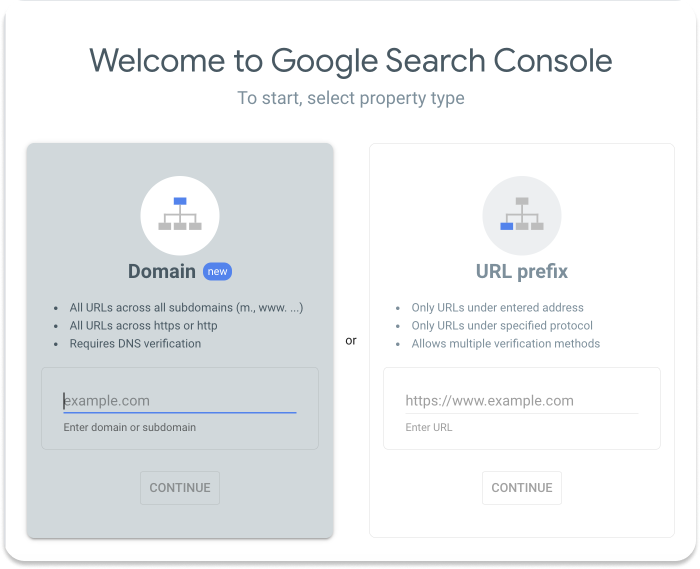
3. You’ll be asked to add your website by selecting a property type. Here’s the difference:
- Domain Property:
- Tracks your entire domain, including all subdomains (e.g., m.example.com, blog.example.com) and protocols (http and https).
- Requires DNS verification.
- Best for large sites with multiple subdomains.
- URL Prefix Property:
- Tracks only the specified URL (e.g., https://www.example.com).
- Allows multiple verification methods (e.g., HTML file, meta tag).
- Ideal for tracking specific sections of your site.
4. After choosing your property type, you’ll be asked to confirm ownership of that property. If you select a domain property, you’ll be prompted to verify domain ownership via DNS record. If you select a URL prefix property, you’ll be prompted to verify domain ownership via HTML file upload, HTML tag, Google Analytics, or Google Tag Manager.
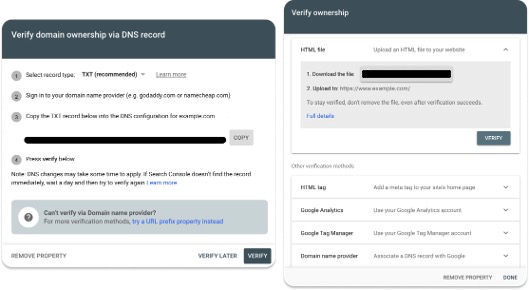
5. If you’ve verified your domain ownership correctly, you will get a success message, and then you’ll be free to explore your new account as you like!

How to delete Google Search Console
You can’t delete Google Search Console, but you can disconnect/remove your website or “property” from the tool. To do that, simply click “Settings” on the left-hand search bar and click “Remove Property” at the bottom of the page in the “About” section.

How to use Google Search Console’s core features
Now that you have a solid understanding of what Google Search Console can do and have your account set up, you might be wondering, “What’s next?” There’s plenty you can do!
As mentioned earlier, GSC provides a wealth of data about website performance. Let’s explore some of the reports and features you can start using.
Create a sitemap
You can create a sitemap for your website by clicking “Sitemaps” under the “Indexing” section. If you don’t see “Sitemaps” right away, click “Indexing” to expand the section.
From there, you can remove outdated or invalid sitemaps from your list of submitted sitemaps. To submit a new one, simply append “sitemap_index.xml” to your URL and click “Submit” under the “Add a new sitemap” option.

Disavow links
Occasionally you’ll want to tell Google’s crawlers to ignore certain backlinks that point to your site. For example, if spam sites point to your website, Google might penalize it, causing it to drop rankings.
To stop that from happening, you can use Google Search Console to tell Google’s crawlers to “Disavow” certain links.
Step 1: Create a list of links to disavow
Start by creating a list of all the web pages or domains you want to disavow in a text file you’ll upload to GSC.
Link file format:
- Specify one URL or domain to disavow per line, such as
example.com - To disavow a domain (or subdomain) prefix it with “
domain:”, for example:domain:example.com - You cannot disavow subpaths. These are sections of a URL that represent a specific folder or directory within a website, like
example.com/enorexample.com/blog - The file must be a text file encoded in UTF-8 or 7-bit ASCII
- The file name must end in .txt
- Maximum URL length is 2,048 characters
- Maximum file size is 100,000 lines and 2MB.
- You can include comments by starting a line with a # mark. Any lines that begin with # will be ignored by Google.
Example of a disavow .txt file:
# Two pages to disavow
http://example.com/stuff/comments.htmlhttp://example.com/stuff/paid-links.html
# One domain to disavow
domain:shadyseo.com
If you’re unsure how to uncover pages and domains to disavow, you can check your backlinks in Google Search Console, too! To check in GSC, click “Links” in the left-hand menu. You can reveal all external sites that link to your website from here by clicking “More” under the “Top linking sites” section.

Check performance
Click “Performance” on the left sidebar to reveal your website’s performance report. From here you can dig into the data to understand everything––from the types of search queries people use to discover your site to your site’s average position on SERPs.
The upper half of the performance report reveals a line chart that reveals your website’s clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position. This report is filterable by time, query, page, country, and device.

You’ll find more data to dig into underneath the line chart. Here, you can see the clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position connected to specific search queries. You can explore the same metrics for pages, countries, devices, search appearance, and dates.

What metrics does Google Search Console measure?
As you can see from the Performance Report, Google Search Console measures plenty of interesting metrics that can give you useful insight into your SEO efforts. Let’s take a look at their core metrics.
Clicks
You can see the total number of clicks to understand how often people click on your website from Google SERPs. You can immediately garner whether your page titles and meta descriptions help you stand out in the search results. If clicks are low, you may need to adjust your titles and meta descriptions.
Your search position also affects how many clicks you’ll get. For example, pages ranked in the top 3 of Google SERPs receive more clicks than those ranking on the second page or further down the first page.
Impressions
Impressions are defined as the amount of times your website or page is shown in search results. For example, if you look at search queries, the number of impressions shows how often your website is shown for that search query on a SERP.
If you want to see how many pages rank for a specific keyword, you can click on the query in your performance report to view a list of the ranked pages.
Likewise, you can click the “Pages” tab next to “Queries” to see all pages that have been crawled by Google’s bot.

Average CTR
Click-through rate, shortened to CTR, is the percentage of people who saw your website on the Google SERP and clicked through to your website. Like clicks, the higher your ranking is on the SERP, the higher your CTR will be.
Also like clicks, you can increase your CTR by rewriting your meta description and page title to make it stand out more in the results.
Average position
Your average position represents the average ranking of a specific search query or page during the selected period.
It’s important to note that your average position isn’t 100% reliable, as different people may see different search results based on factors like location, language, and user behavior. Google tailors results to suit each visitor’s needs. Still, the average position provides useful insight into how your impressions, clicks, and CTR are performing.
Make the most of Google Search Console
Search Console reveals a treasure trove of data and insights you can use to improve website maintenance and performance. With GSC in your marketing toolkit, difficulty climbing SERP rankings will quickly become a thing of the past.